What is the Function of the Switch in Moxa?

Introduction
In the fast-moving world of industrial automation, uninterrupted and reliable communication between devices is non-negotiable. Whether you are running a factory floor, managing a power substation, or operating a transportation control system, your network is the lifeline that keeps operations smooth. At the heart of this network infrastructure lies a critical component the switch.
For industrial applications, general-purpose networking hardware isn’t always enough. This is where Moxa steps in. Known for designing robust and highly reliable industrial networking equipment, Moxa switches are engineered to operate in challenging environments with high electromagnetic interference, temperature extremes, and heavy vibration. But beyond durability, these switches serve an essential role: enabling seamless communication between devices while optimizing network performance.
In this blog, we’ll break down the exact function of a switch in Moxa, how it fits into industrial networking, key types and features, and real-world applications. We’ll also cover common misconceptions, best practices, and frequently asked questions so you’ll have a complete, practical, and SEO-rich resource.
Understanding the Basics – What Is a Network Switch?
A network switch is a device that connects multiple devices (like PLCs, HMIs, industrial PCs, and IP cameras) within a Local Area Network (LAN) and facilitates communication by forwarding data to the correct destination.
Think of it as a traffic controller in the networking world directing data packets only where they need to go instead of broadcasting them to every device. This improves bandwidth efficiency, reduces network congestion, and ensures that critical industrial control data reaches the right place without delays.
How Moxa Switches Work
While the core principle is the same as any network switch, Moxa switches are tailored for industrial environments with additional reliability, redundancy, and management features. Here’s how they function:
1. Device Connection – Multiple devices connect to the switch through Ethernet ports.
2. Data Packet Inspection – Each incoming data packet contains source and destination information (MAC address).
3. Intelligent Forwarding – The switch reads the destination MAC address and sends the packet only to the relevant device.
4. Traffic Segmentation – Reduces unnecessary data flooding and allows simultaneous data transfers without interference.
5. Industrial Protocol Support – Moxa switches support protocols like Modbus TCP, EtherNet/IP, and PROFINET, making them ideal for factory automation.
The Core Functions of a Switch in Moxa
a. Efficient Data Forwarding
The primary role of a Moxa switch is to forward data only to the intended recipient, optimizing network bandwidth and preventing overload.
b. Network Segmentation
By dividing the network into smaller collision domains, Moxa switches help improve performance and security.
c. VLAN Support
Many Moxa switches allow Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) configurations, enabling logical segmentation for security and traffic management.
d. Redundancy and Reliability
Moxa switches often include redundancy protocols like Turbo Ring and Turbo Chain, ensuring sub-50ms recovery in case of network failure.
e. Quality of Service (QoS)
Prioritizes time-sensitive data like control signals over less critical traffic, ensuring real-time performance.
Types of Moxa Switches
Moxa offers a wide range of switches for different industrial needs:
|
Type |
Description |
Example Series |
|
Plug-and-play devices with no configuration required, ideal for simple setups. |
EDS-200, EDS-300 |
|
|
Allow advanced configuration, monitoring, VLANs, and redundancy. |
EDS-500, EDS-600 |
|
|
PoE Switches |
Provide Power over Ethernet to devices like IP cameras and wireless APs. |
EDS-P Series |
|
Rackmount Switches |
Designed for larger control rooms with high port density. |
ICS-G Series |
Why Industrial Environments Need Moxa Switches
Unlike office networks, industrial networks face unique challenges:
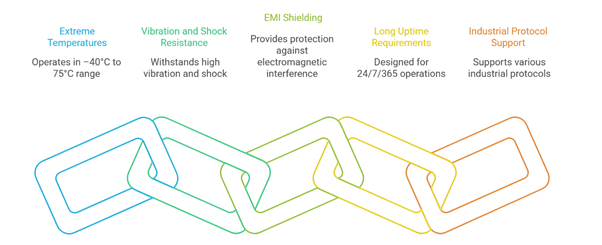
Moxa designs switches that meet these demands without compromising network performance.
Real-World Applications of Moxa Switches
1. Factory Automation – Connecting PLCs, HMIs, and sensors in a production line.
2. Transportation Systems – Managing signaling and surveillance in rail and traffic control.
3. Energy Sector – Monitoring power grids and substations with IEC 61850 compliance.
4. Oil & Gas – Offshore rigs and pipelines requiring reliable communication.
5. Marine & Offshore – Withstanding humidity, salt spray, and vibrations.
Key Features That Set Moxa Switches Apart
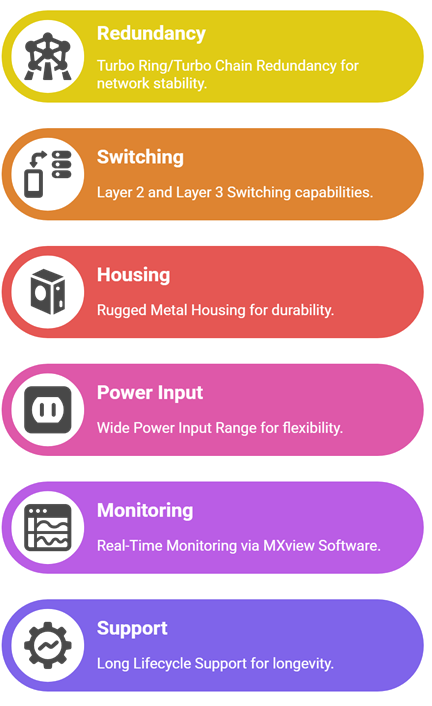
Best Practices for Using Moxa Switches
· Use managed switches for complex networks requiring monitoring.
· Enable QoS to prioritize critical control signals.
· Implement redundancy protocols to avoid downtime.
· Keep firmware updated for security and performance.
· Use industrial-grade cabling for harsh environments.
Conclusion
The function of the switch in Moxa goes far beyond just connecting devices it’s about ensuring efficient, reliable, and secure data flow in industrial environments where downtime isn’t an option. Whether it’s enabling real-time control on a production line or ensuring seamless communication in a power grid, Moxa switches are engineered to keep industrial networks running at peak performance.
By understanding how these switches work, their types, and their features, you can design a robust network infrastructure that meets both current and future operational demands.







