How Long Does Nitazoxanide Take to Work in the Body?

Parasitic and viral infections can cause significant discomfort and health complications if left untreated. Nitazoxanide 500 mg is a widely used medication that treats a range of infections, particularly protozoal and parasitic infections like Giardia, Cryptosporidium, and certain viral infections. Patients often wonder how quickly it works and when they can expect relief. Understanding the mechanism, absorption, action, and factors affecting its effectiveness is crucial for safe and effective use. This article explores how long Nitazoxanide takes to work in the body, its pharmacological action, clinical effectiveness, and key considerations for optimal results.
What Is Nitazoxanide?
Nitazoxanide is a broad-spectrum antiparasitic and antiviral medication. It belongs to the thiazolide class of drugs and is effective against a variety of protozoa, helminths, and some viruses. Its broad activity makes it a first-line treatment for intestinal parasitic infections, including:
-
Giardiasis – Caused by Giardia lamblia, leading to diarrhea, abdominal pain, and malabsorption.
-
Cryptosporidiosis – Caused by Cryptosporidium parvum, often resulting in watery diarrhea and dehydration.
-
Other Protozoal and Helminthic Infections – Nitazoxanide is sometimes used off-label for infections such as Blastocystis hominis.
Nitazoxanide is available in tablets, oral suspension, and pediatric formulations, allowing flexible dosing for adults and children.
How Nitazoxanide Works in the Body
To understand how fast Nitazoxanide works, it is important to know its mechanism of action.
1. Targeting Parasite Metabolism
Nitazoxanide acts by interfering with the energy metabolism of parasites. It inhibits the enzyme pyruvate:ferredoxin oxidoreductase (PFOR), which is essential for anaerobic energy production in protozoa and certain helminths. Without this enzyme, parasites cannot produce the energy needed to survive, grow, or reproduce.
2. Disrupting Viral Replication
Nitazoxanide also has antiviral properties. It interferes with the maturation of viral proteins, preventing viruses from replicating efficiently within host cells. This dual action—antiparasitic and antiviral—makes Nitazoxanide unique among treatments for gastrointestinal and systemic infections.
3. Rapid Absorption and Distribution
After oral administration, Nitazoxanide is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract. It is metabolized into its active metabolite, tizoxanide, which circulates in the bloodstream and accumulates in tissues, including the gut wall, liver, and kidneys—common sites of parasitic infection.
This absorption and distribution allow the drug to reach the infection site quickly, initiating its therapeutic effect within hours.
Onset of Action
The onset of Nitazoxanide depends on several factors:
1. Type of Infection
-
Giardiasis: Patients often experience symptom relief within 1–2 days of starting treatment, though the full eradication of parasites may require completing the entire course.
-
Cryptosporidiosis: Symptom improvement may take 2–5 days, depending on the severity of infection and the patient’s immune status.
-
Other Protozoal Infections: The response time can vary; mild infections may respond quickly, while severe infections may need longer treatment.
2. Dosage and Duration
The standard adult dose for most parasitic infections is 500 mg twice daily for 3 days, while pediatric doses are calculated based on body weight. Completing the full course ensures that all parasites are eliminated and reduces the risk of reinfection or recurrence.
3. Individual Factors
Factors such as age, body weight, liver function, gastrointestinal health, and immune status can influence how quickly Nitazoxanide works. Patients with weakened immunity or underlying conditions may experience slower symptom resolution.
Pharmacokinetics: How Long Nitazoxanide Stays Active in the Body
Nitazoxanide has favorable pharmacokinetics that support its rapid and sustained action:
-
Absorption: Rapid in the gastrointestinal tract, with peak plasma concentration achieved within 1–4 hours.
-
Metabolism: Converted into the active metabolite tizoxanide, which mediates its therapeutic effects.
-
Half-Life: Tizoxanide has a half-life of approximately 1.5–2 hours, but its prolonged tissue penetration ensures continued activity even after plasma levels decrease.
-
Excretion: Eliminated mainly through the urine and feces, ensuring effective clearance of parasites.
These properties explain why Nitazoxanide can be administered in short courses (usually 3 days) while still achieving significant therapeutic effects.
Factors Affecting the Speed of Action
Several factors can influence how quickly Nitazoxanide works:
1. Severity of Infection
-
Mild infections respond faster, often showing improvement within 24–48 hours.
-
Severe infections with high parasite loads may take longer to resolve.
2. Food Intake
-
Nitazoxanide is better absorbed with food, particularly high-fat meals. Taking it on an empty stomach may slightly delay its action.
3. Coexisting Conditions
-
Patients with liver or kidney impairment may experience slower metabolism or clearance, affecting the speed of action.
-
Immune-compromised individuals may take longer to recover, even though the drug kills the parasites.
4. Adherence to Dosage
-
Skipping doses or not completing the prescribed course can delay recovery and reduce the overall effectiveness of Nitazoxanide.
Clinical Effectiveness
Clinical studies have demonstrated Nitazoxanide’s efficacy in treating parasitic infections:
-
Giardia lamblia infections: Cure rates of 85–95% after a 3-day course.
-
Cryptosporidium infections: Symptom improvement observed in majority of patients within 2–4 days, with parasite clearance confirmed after completing treatment.
-
Other protozoal infections: Varying success rates, but generally high efficacy in clinical trials.
Patients often report reduced diarrhea, abdominal pain, bloating, and nausea within the first 48–72 hours, even though completing the full course is necessary for complete eradication.
Safety and Side Effects
Nitazoxanide is generally well-tolerated. Common side effects include:
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Stomach pain or cramps
-
Headache
-
Mild diarrhea
-
Temporary discoloration of urine (rare)
Severe side effects are uncommon but may include allergic reactions. Most side effects are temporary and resolve after completing treatment.
Precautions
-
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: Nitazoxanide is generally considered safe but should be used under medical supervision.
-
Liver or Kidney Disease: Dose adjustments may be necessary for patients with impaired organ function.
-
Drug Interactions: Nitazoxanide has a low potential for drug interactions, but it’s still advisable to consult a healthcare provider before combining it with other medications.
Tips to Maximize Effectiveness
-
Take With Food: Enhances absorption and efficacy.
-
Complete the Full Course: Even if symptoms improve quickly, completing the treatment ensures total eradication of parasites.
-
Stay Hydrated: Helps relieve symptoms like diarrhea and supports overall recovery.
-
Practice Hygiene: Wash hands, clean fruits and vegetables, and avoid contaminated water to prevent reinfection.
Conclusion
Nitazoxanide is a fast-acting, broad-spectrum antiparasitic and antiviral medication. Its mechanism of action—disrupting parasite energy metabolism and inhibiting viral replication—allows it to work effectively within the body, often providing symptom relief within 1–3 days for most infections. Factors such as the type and severity of infection, dosage, food intake, and individual health influence the exact timing.
Its favorable pharmacokinetics, short-course dosing, and high efficacy make it an ideal choice for treating protozoal infections like Giardia and Cryptosporidium, improving patient compliance and outcomes. By understanding how Nitazoxanide works and the factors that affect its action, patients can use it safely and effectively to restore health and prevent complications from parasitic infections.
Nitazoxanide is more than just a medication; it is a reliable tool in modern medicine for quickly controlling infections, alleviating symptoms, and supporting recovery, ensuring patients regain normal function and well-being efficiently.
Categories
Read More
When I first started navigating property markets across the UK I quickly realised that most new investors were jumping in without fully understanding the landscape They were buying based on gut feelings hearsay or rushed conversations with agents Real Estate Investment Advisory Firms have since become a cornerstone in preventing these early missteps offering the kind of structured decision...

"Executive Summary North America Medical Grade Silicone Market : CAGR Value The medical grade silicone market is expected to witness market growth at a rate of 6.04% in the forecast period of 2022 to 2029. The market insights and market analysis about industry, made available in this North America Medical Grade Silicone Market research report are rooted upon SWOT analysis...

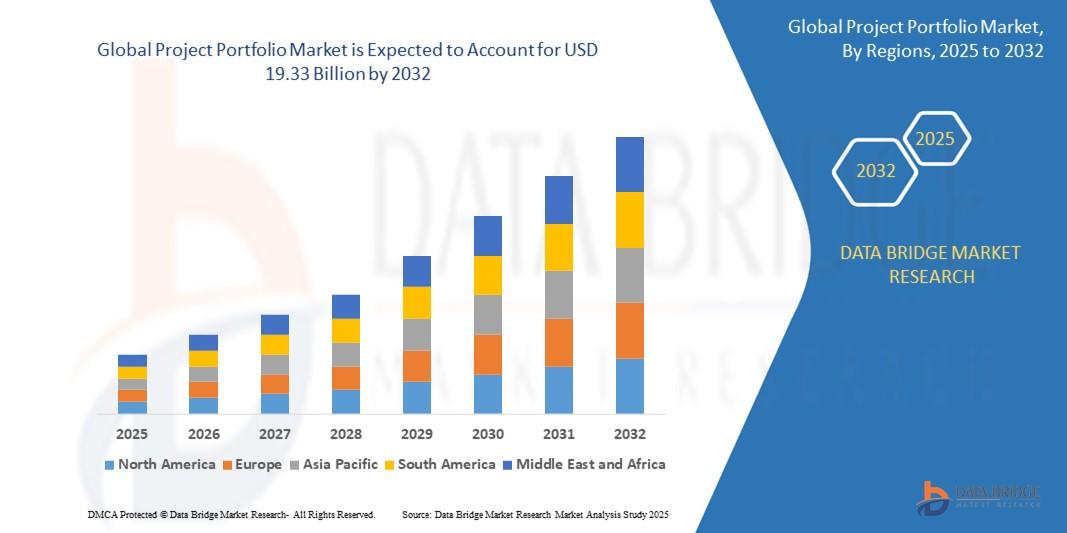
"In-Depth Study on Executive Summary Project Portfolio Market Size and Share The global project portfolio market size was valued at USD 7.69 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 19.33 billion by 2032, at a CAGR of 12.20% during the forecast period As the high quality Project Portfolio Market survey report has precise and accurate analysis of market...
Executive Summary Pet Accessories Market : The global Pet Accessories market was valued at USD 10.98 billion in 2024 and is expected to reach USD 17.63 billion by 2032, During the forecast period of 2025 to 2032 the market is likely to grow at a CAGR of 6.10%, primarily driven by the increasing pet humanization trend and rising disposable income. The...

Looking for reliable Custom Software Development Companies in Saudi Arabia? Discover the Top 15 awarded firms known for innovation, quality, and trust. This curated list helps you partner with the right software experts to drive your digital success.




