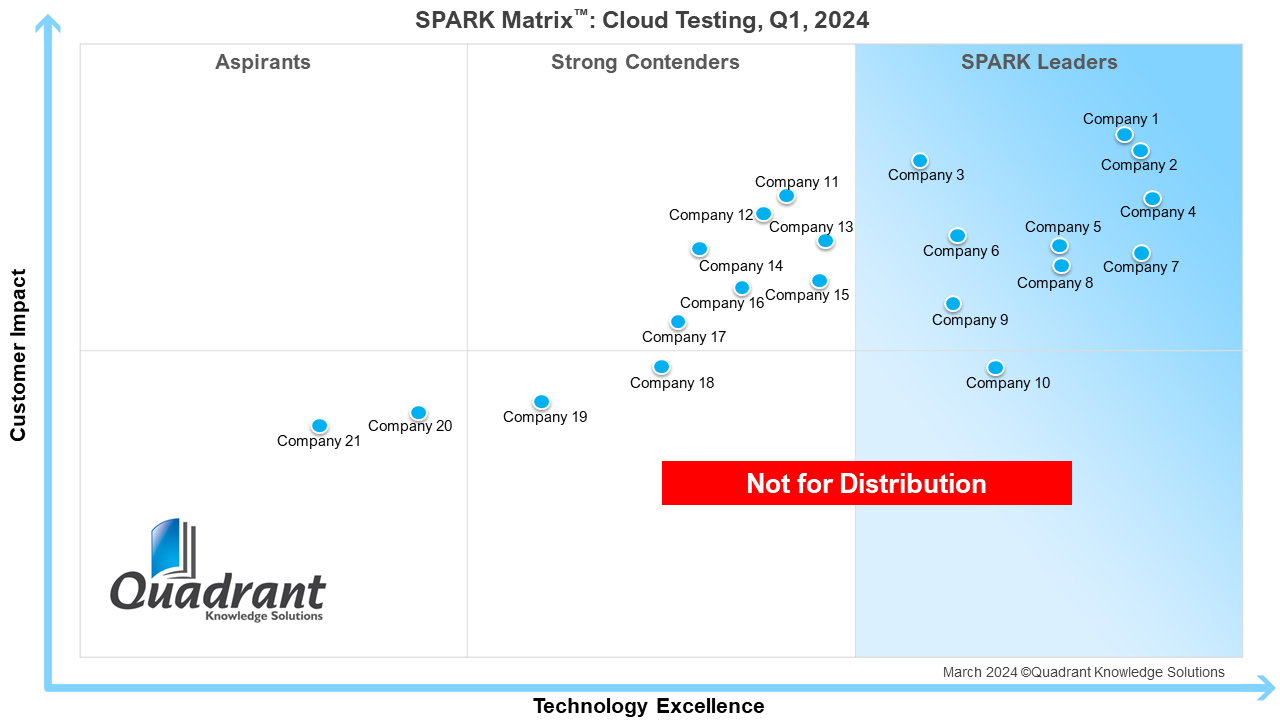
SPARK MATRIX Cloud Testing Explained: Boosting Quality, Speed, and Scalability
In today’s digital-first business landscape, software applications are the driving force behind innovation and customer engagement. Ensuring their reliability, performance, and scalability has become paramount for organizations across industries. This is where Cloud Testing emerges as a cornerstone of modern software development—empowering teams to test smarter, faster, and more efficiently in the cloud.
What Is Cloud Testing?
Cloud Testing is the practice of leveraging cloud computing resources and infrastructure to test applications, services, and systems. Instead of relying on traditional, on-premises environments, teams can utilize scalable cloud-based environments to simulate real-world conditions, validate performance, and ensure seamless functionality across platforms and geographies.
By integrating automation, AI, and continuous delivery practices, Cloud Testing enables organizations to detect and resolve issues early in the development cycle—reducing costs, improving agility, and accelerating time-to-market.
Key Components of Cloud Testing
Modern Cloud Testing goes beyond conventional quality assurance. It integrates multiple aspects of the testing lifecycle, including:
- Cloud Infrastructure Testing
Verifies that the underlying cloud environment—servers, storage, and network configurations—functions as expected. This ensures high availability, scalability, and data integrity. - Test Automation
Automates repetitive test cases across different builds and environments, accelerating test execution while minimizing manual effort and human error. - API and Service Testing
Validates communication between microservices, APIs, and external integrations to guarantee consistent performance and interoperability across distributed systems. - End-to-End Testing
Ensures that entire workflows, from front-end interfaces to backend systems, operate seamlessly in cloud-native applications. - Test Environment Management
Cloud-based test environments can be provisioned and decommissioned on demand, allowing QA teams to maintain flexibility and control while reducing infrastructure costs.
Benefits of Cloud Testing
The rise of Cloud Testing is fueled by the need for faster innovation and scalable quality assurance. Some of its most significant benefits include:
- Scalability and Flexibility: Cloud infrastructure allows organizations to scale testing resources up or down based on project demands—ideal for handling variable workloads.
- Cost Efficiency: Eliminates the need for expensive on-premises hardware and maintenance by adopting a pay-as-you-go model.
- Global Accessibility: Cloud-based platforms allow distributed teams to collaborate seamlessly, regardless of location or time zone.
- Accelerated Time-to-Market: Automated testing and parallel execution shorten development cycles, helping organizations release updates more frequently.
- Enhanced Performance Testing: Teams can simulate thousands of concurrent users and real-world traffic conditions to identify performance bottlenecks early.
- Security and Compliance: Continuous cloud testing helps detect vulnerabilities and enforce security policies, strengthening the application’s defense posture.
Cloud Testing and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD)
In the DevOps era, Cloud Testing has become an integral part of CI/CD pipelines. Automated tests are executed continuously throughout the software development lifecycle, ensuring that each code change is validated before deployment. This continuous validation reduces the risk of production failures and supports a culture of rapid iteration and innovation.
Cloud Testing platforms also integrate seamlessly with development tools, enabling teams to monitor test results, analyze performance trends, and make data-driven quality improvements.
Addressing Challenges in Cloud Testing
While the benefits are immense, implementing Cloud Testing comes with its own set of challenges:
- Data Privacy and Security: Ensuring sensitive data remains protected during cloud-based testing is crucial.
- Environment Compatibility: Differences in cloud providers or configurations may cause inconsistencies in test results.
- Cost Management: Without proper oversight, pay-per-use models can lead to unexpected expenses.
These challenges can be mitigated through careful planning, using secure testing environments, implementing data anonymization, and leveraging cost-monitoring tools.
The Future of Cloud Testing
As emerging technologies such as AI, ML, and edge computing reshape software development, Cloud Testing will continue to evolve. AI-driven test automation, predictive analytics, and intelligent test data management will redefine how teams validate software at scale.
Moreover, as applications increasingly adopt microservices and multi-cloud architectures, Cloud Testing will play a pivotal role in ensuring seamless integration and optimal performance across distributed ecosystems.
Conclusion
Cloud Testing is no longer an optional component of the software development lifecycle—it’s a strategic enabler of digital transformation. By combining scalability, automation, and analytics, it empowers organizations to deliver high-quality, secure, and performant applications faster than ever before.
As enterprises continue to innovate in the cloud, adopting a comprehensive Cloud Testing strategy will be essential to maintaining agility, ensuring reliability, and driving continuous business success.