Rugged Touch Screen Display vs. Rugged Touch Screen Monitor: Choosing the Best Rugged Display for Your Needs
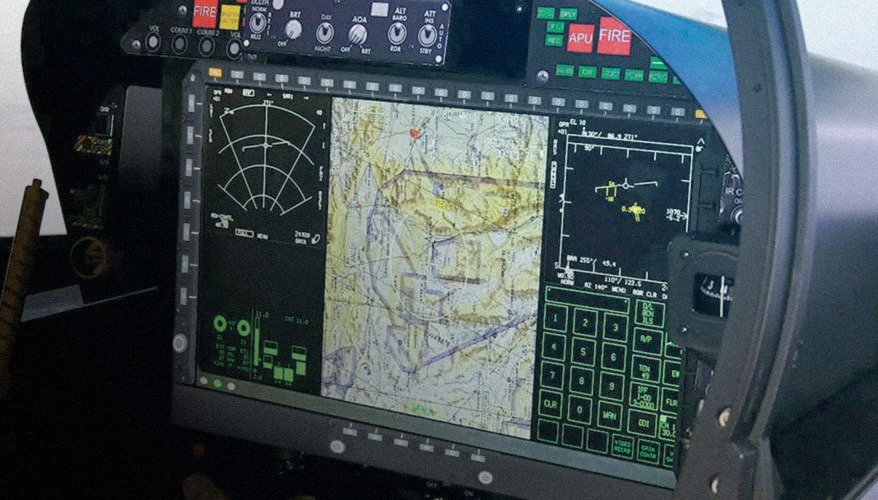

Selecting the right rugged display always becomes challenging for different industries. Whether used in manufacturing, military operations, transportation or outdoor fieldwork rugged displays and rugged monitors are manufactured to withstand tough conditions. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they serve different needs and applications. Understanding the distinctions between a rugged touch screen display and a rugged touch screen monitor can help you choose the best solution for your specific environment and operational goals.
Differences Between Rugged Displays and Monitors
Choosing the ideal rugged display starts with identifying the differences between the types available and how each fits into different operational settings. While both rugged touch screen monitors and displays are built to endure extreme elements, their functionality, integration, and use cases vary. Below, we’ll explore these differences to help you align your choice with your work requirements.
Know the Purpose Behind Each Device
The most fundamental difference between a rugged touch screen display and a rugged touch screen monitor lies in their intended role within a system. A display typically functions as a standalone embedded component within a device or a machine. It is often used in custom equipment, kiosks, and vehicles where space, design, and direct integration are important. These displays usually require external computing systems to function.
On the other hand, a rugged touch screen monitor is a complete unit that includes housing and connectivity options such as HDMI, DisplayPort, or USB. Monitors are ready-to-use peripherals that can be connected to various systems, including mobile workstations, laptops, or fixed installations in industrial control rooms. They are ideal for users who need an easy-to-deploy, plug-and-play, rugged display solution.
Evaluate the Installation Environment
When selecting the right rugged display, it is useful to consider the intended use location. A rugged touch screen monitor is best mounted on a desktop or a panel located in a laboratory, control room, or mobile command center. The rugged monitor has built in enclosures that protect the interior from shock, dust, and water.
A rugged touch screen display, by contrast, is commonly embedded into machinery or vehicle dashboards. These displays are favored in applications where size, weight, and design flexibility are critical. If your equipment requires a custom enclosure or must comply with tight spatial constraints, an embedded rugged touch screen display may be the optimal choice.
Consider the Connectivity and Compatibility Needs
Another important difference is the number of ways to connect. Most rugged touchscreen monitors come with standard ports that allow you to connect them easily to various computer systems. Some of these are VGA, HDMI, USB for touch controls, and legacy ports that work with older systems. This means they work well together and are easy to integrate with existing systems.
Rugged touch screen displays, on the other hand, often require more technical setup. Because they are usually embedded within larger systems, they may be designed with custom interfaces or minimal connectivity, relying on internal wiring. Choosing a display over a monitor might require additional development resources, especially when integrating into specialized equipment.
Assess Maintenance and Accessibility
Ease of maintenance and accessibility also impact your long-term satisfaction with the product. Rugged touch screen monitors can be easily replaced or serviced because they are standalone units. This modularity is a major benefit for operations that value uptime and need to minimize disruption during maintenance.
Rugged touch screen displays, particularly those embedded into systems, are harder to access once installed. Repairs or replacements may require disassembling parts of the machine or device. If your environment demands easy servicing and quick swaps, a rugged monitor might be a more practical investment.
Choose Based on Your Application Requirements
The specific use case should ultimately guide your decision. For example, a rugged touch screen monitor is well-suited for applications like field-based data entry, warehouse logistics, mobile diagnostics, or portable testing units. Its ease of use and wide compatibility make it ideal for field workers and mobile teams.
Conversely, a rugged touch screen display is a preferred choice in environments where space is limited or where the display must seamlessly integrate with proprietary systems. Think of mining vehicles, defense equipment, or automated manufacturing machines where customization is a top priority.
Explore High-Performance Options Like the Rugged Display Line
For those looking to strike a balance between flexibility, durability, and advanced functionality, exploring premium product lines like the Rugged Display series can be worthwhile. These products combine the robust features of both rugged monitors and rugged displays, offering high brightness, glove-compatible touchscreens, and a variety of mounting options. Designed for industrial and military-grade applications, they deliver long-term performance even in the harshest environments.
Whether you need a rugged touch screen monitor for its plug-and-play convenience or a rugged touch screen display for full customization, the Rugged Display lineup ensures your investment is protected against shock, vibration, moisture, and extreme temperatures.
Conclusion
Choosing the right rugged display is not just about choosing one that claims to be tough. It is about choosing one that fits your exact workflow, location of installation, and connectivity. Knowing the functional and practical differences between rugged touch screen displays vs rugged touch screen monitors will allow you to make an educated choice that will maximize productivity, while ensuring durability under all conditions, and will minimize downtime.