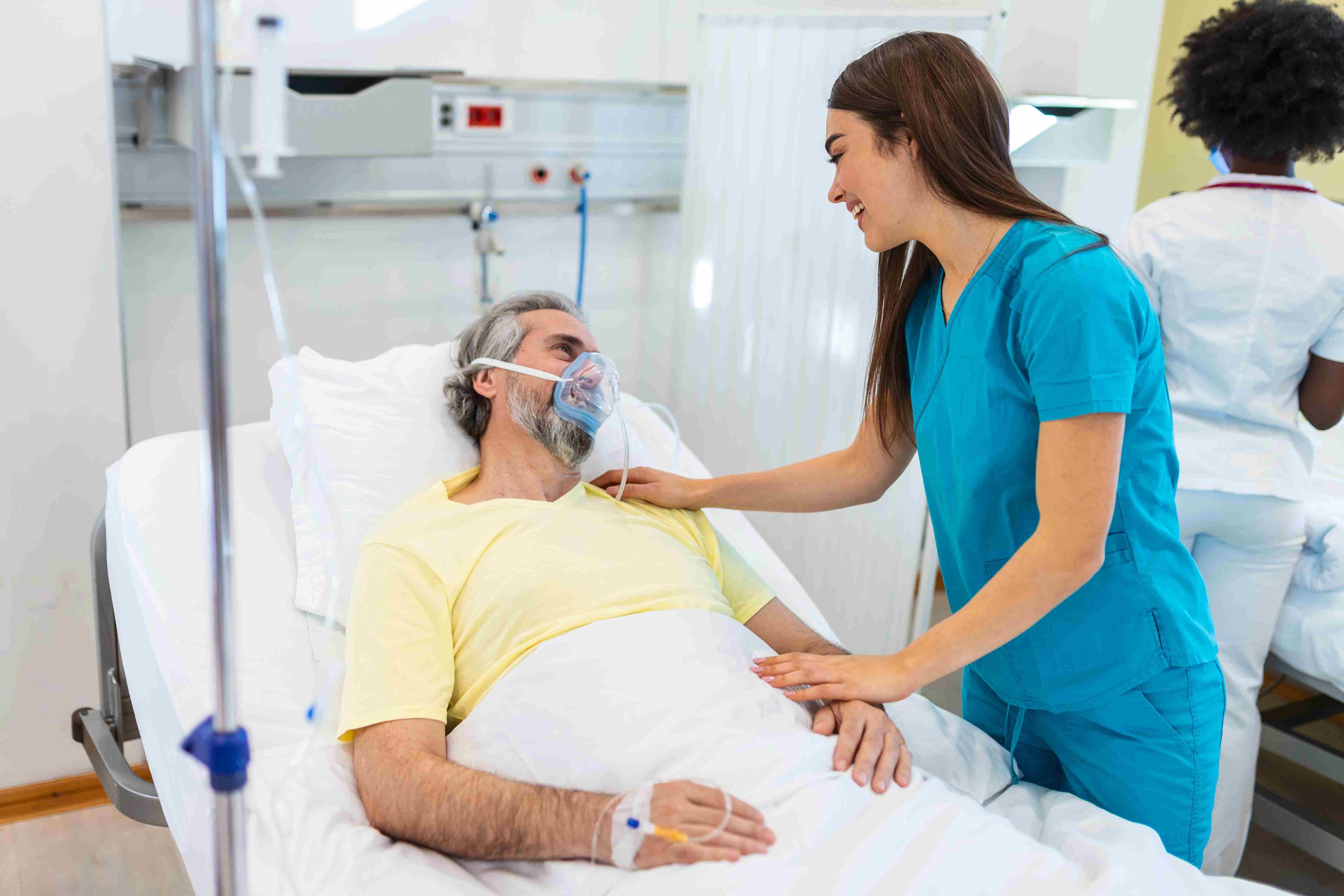
Biometric Driver Authentication: Enhancing Automotive Security
Biometric Driver Authentication verifies the driver’s identity using biometric features such as fingerprints, facial recognition, or iris scans. This ensures secure vehicle operation, prevents unauthorized use, and enables personalized settings for driver comfort. Growing demand for vehicle security and smart access solutions is driving adoption across modern automotive platforms.
Identification vs. Authentication: What's the Difference?
It's a subtle but crucial distinction:
-
Identification answers the question: "Who are you?" When a facial recognition system sees you and loads your seat and mirror presets, it is identifying you from a list of known users.
-
Authentication answers the question: "Are you really who you say you are?" It is a verification step. When you use your fingerprint to authorize an in-car payment, you are authenticating your identity to approve that specific transaction.
Authentication is the security check required before a critical function is performed.
Key Use Cases for Biometric Authentication
The demand for robust driver authentication is driven by several key applications that are becoming common in modern vehicles.
-
Secure Vehicle Start: This is the most fundamental use case. While a key fob can be stolen or its signal relayed, a car equipped with biometric authentication might require a valid fingerprint on the start button before the powertrain will engage. This provides a powerful second layer of anti-theft security.
-
In-Car Payments: The connected car is rapidly becoming a payment platform. Drivers can pay for EV charging, parking, tolls, or even a drive-thru order directly from the dashboard. To prevent fraud, these transactions must be securely authenticated. A quick glance at an iris scanner or a touch of a fingerprint sensor provides a seamless and secure method, similar to using Face ID for Apple Pay.
-
Accessing Secure Profiles: Many cars now allow for multiple driver profiles. Some of this profile data can be sensitive, such as saved home and work addresses, contacts, or linked digital wallet information. Biometric authentication can be used to protect access to these personal profiles, ensuring a passenger or valet cannot access the primary driver's private data.
-
Activating Advanced Features: In the future, a car's most advanced features, like a high-performance "track mode" or certain autonomous driving capabilities, may require biometric authentication to ensure they are being used by the authorized, primary driver.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q1: What is the difference between biometric identification and authentication? A1: Identification is about recognizing who you are from a group of known users (e.g., loading your profile). Authentication is a specific security check to verify your identity before allowing a sensitive action (e.g., approving a payment).
Q2: Why is authentication needed inside the car? A2: It is needed to secure critical functions. As you start to perform financial transactions (in-car payments) and store sensitive personal data in your vehicle's infotainment system, authentication is required to prevent fraud and protect your privacy.
Q3: Which biometric is best for in-car payments? A3: For high-security transactions, facial recognition and especially iris scanning are considered top-tier methods. They are extremely difficult to spoof and can be performed quickly and easily by the driver.
Biometric driver authentication is the security backbone of the software-defined vehicle. It is the essential technology that builds trust between the driver and the car's powerful new capabilities, ensuring that as our vehicles become smarter and more connected, they also become more personally and digitally secure.
More Related Report
E-Drive for Automotive Market Size