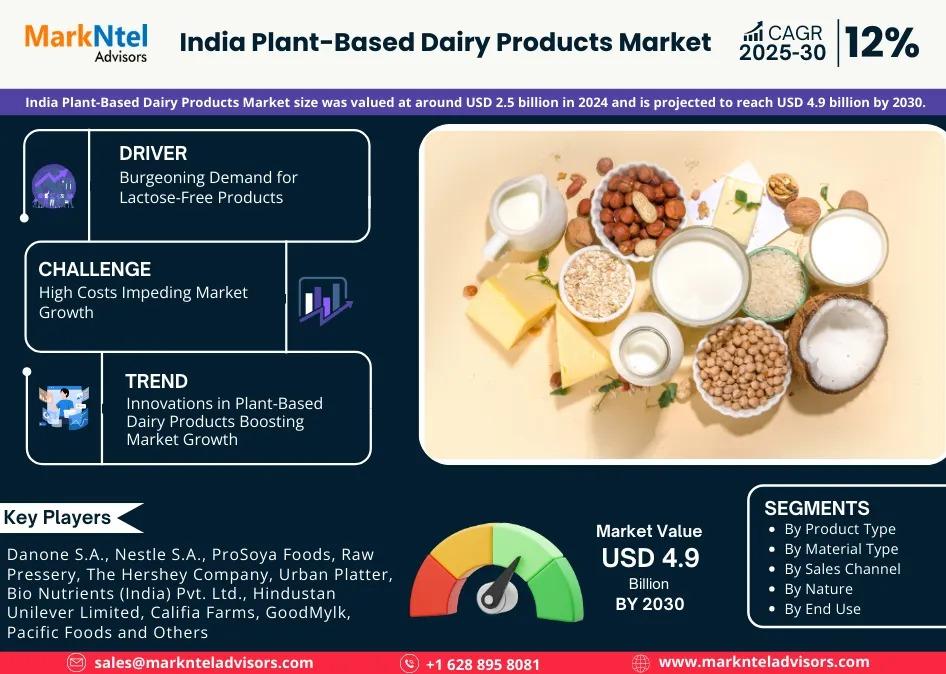
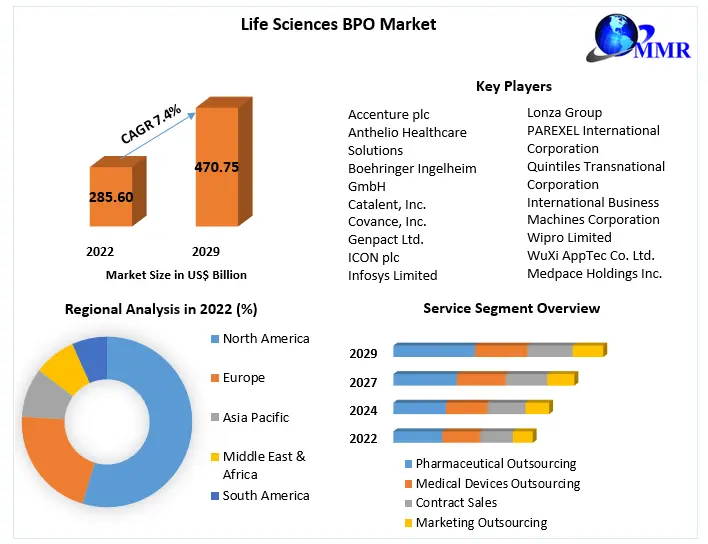
Understanding Gestational Diabetes Causes and Treatment

Pregnancy is a time of excitement and change, but it can also bring unexpected health challenges. One of the conditions that some expectant mothers face is gestational diabetes, a type of diabetes that develops during pregnancy. While it may sound alarming, with the right care and treatment, most women are able to manage it successfully and deliver healthy babies. Understanding the causes, risks, and treatment options is the first step toward protecting both mother and child.
What Is Gestational Diabetes?
Gestational diabetes occurs when a woman’s body cannot produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar during pregnancy. Insulin is a hormone that helps glucose move from the bloodstream into cells to be used for energy. During pregnancy, the placenta releases hormones that naturally increase blood sugar. In most cases, the body produces more insulin to balance this effect, but sometimes it isn’t enough, leading to higher glucose levels.
Risk Factors to Consider
Not every pregnant woman will develop gestational diabetes, but some are more likely than others. Common risk factors include:
● Being overweight before pregnancy
● A family history of type 2 diabetes
● Previous pregnancy with gestational diabetes
● Being older than 25 during pregnancy
● Having polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
● Giving birth to a baby weighing over 9 pounds in the past
Even women without these risk factors can develop the condition, which is why routine screening during pregnancy is essential.
Potential Complications
If not managed properly, gestational diabetes can cause health concerns for both the mother and the baby. Some of these include:
● For the Baby: Babies may grow larger than normal (macrosomia), increasing the likelihood of a cesarean delivery. They may also experience low blood sugar shortly after birth or face a higher risk of obesity and type 2 diabetes later in life.
● For the Mother: Women may develop high blood pressure or preeclampsia, both of which can complicate pregnancy. There’s also a higher chance of developing type 2 diabetes in the years following pregnancy.
The good news is that most of these risks can be greatly reduced through proper care and lifestyle changes.
Final Thoughts
Gestational diabetes can feel overwhelming at first, but with the right knowledge and support, it can be managed effectively. By focusing on healthy lifestyle choices, regular monitoring, and medical guidance, mothers can protect their health while giving their babies the best start in life. Pregnancy is a journey full of changes, and while this condition adds a layer of complexity, it doesn’t have to define the experience.