The Unsung Hero of Automotive Component Protection
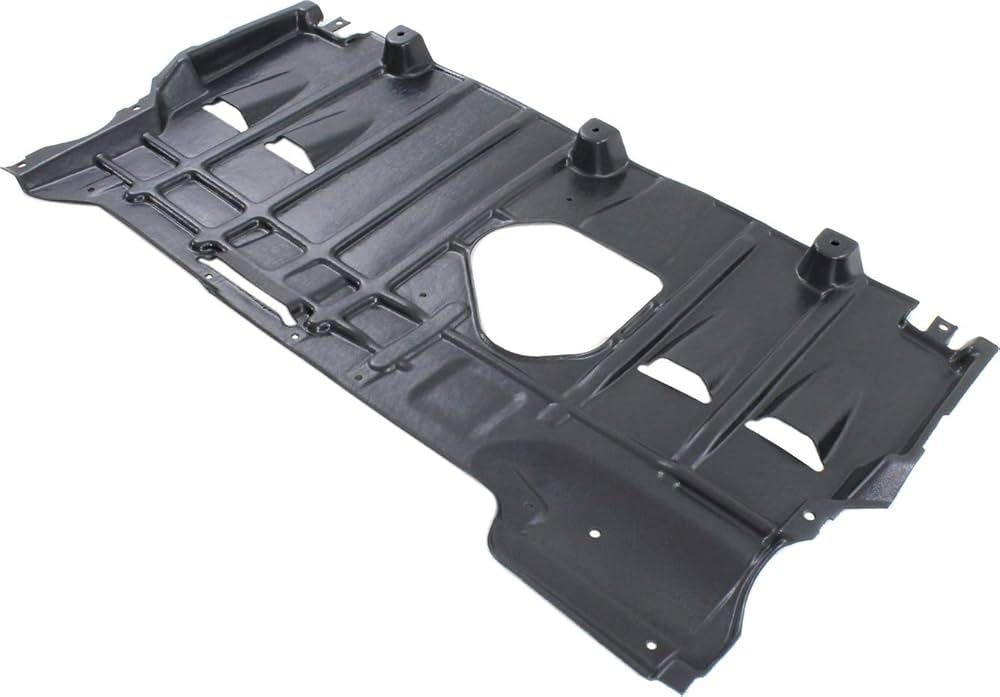

Often overlooked by the average car owner, the Splash Shield is a critical component that serves as the unsung hero of a vehicle's undercarriage and engine bay. This protective panel, typically located beneath the engine and behind the front bumper, is meticulously designed to perform a vital function: safeguarding essential mechanical and electrical components from a constant barrage of environmental threats. It acts as a primary barrier against water, mud, road salt, gravel, and other debris that can be kicked up from the road surface. By preventing these corrosive and damaging elements from reaching the engine, alternator, belts, pulleys, and sensitive wiring, the splash shield plays an instrumental role in preventing premature wear and tear, reducing the risk of costly repairs, and ultimately enhancing the overall longevity and reliability of the vehicle.
Splash shields are engineered from a variety of durable materials, each selected for its specific properties to withstand the harsh under-vehicle environment. The most common materials are rigid, high-impact plastics such as high-density polyethylene (HDPE) or polypropylene, which are favored for their light weight, resistance to corrosion, and cost-effective manufacturing through processes like injection molding. These materials offer an excellent balance of flexibility and strength, allowing them to absorb minor impacts without cracking. In some heavy-duty or high-performance applications, splash shields may be constructed from metal alloys like aluminum or steel, which provide superior impact resistance and rigidity. The choice of material is a careful engineering decision, balancing factors like vehicle weight targets, aerodynamic considerations, durability requirements, and production costs to deliver optimal protection for the specific vehicle model.
The consequences of driving with a damaged or missing splash shield can be far more significant than many realize. Without this protective layer, the engine bay is left exposed to the elements, which can lead to a host of problems. Water splashing onto hot engine components can cause thermal stress, while moisture can lead to electrical shorts in sensitive sensors and connectors. Debris can get caught in serpentine belts and pulleys, causing them to shred or fail, potentially leading to a breakdown. In regions with harsh winters, road salt can rapidly accelerate the corrosion of the vehicle's frame, subframe, and engine components. Furthermore, the splash shield is often an integral part of a vehicle's aerodynamic design, helping to smooth airflow under the car. Its absence can create drag, negatively impacting fuel efficiency and handling at higher speeds.