Cochlear implant surgery is a life-altering procedure that offers individuals with severe to profound hearing loss the potential to regain a sense of sound and improve their ability to communicate. This innovative technology bypasses damaged hair cells within the inner ear, directly stimulating the auditory nerve and sending electrical signals to the brain for sound interpretation.
How Cochlear Implants Work
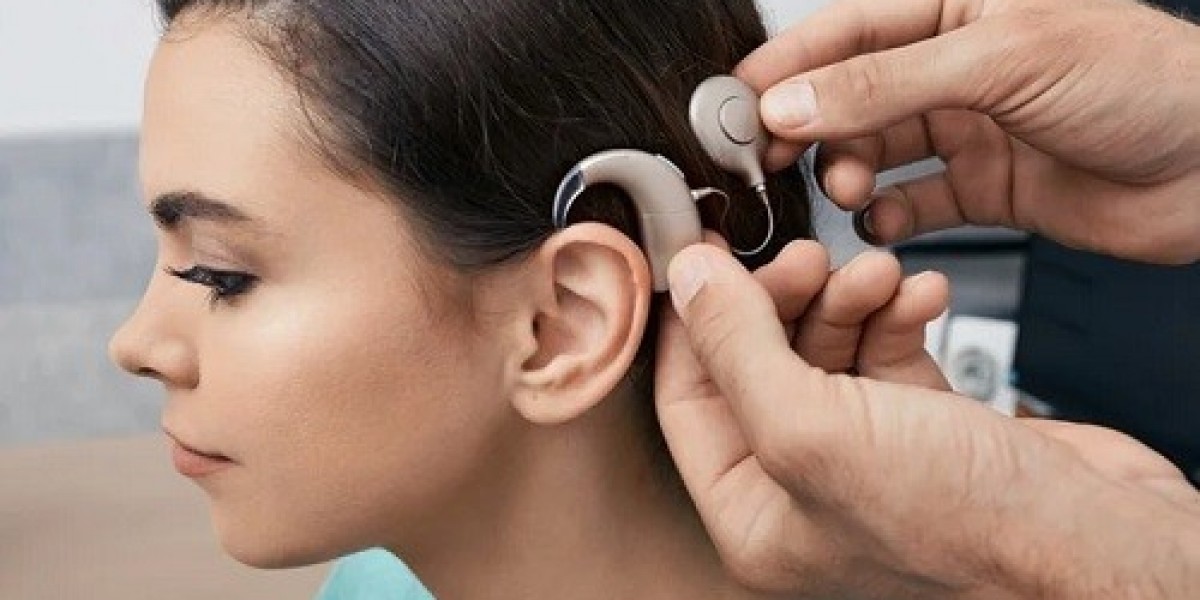
A cochlear implant consists of two main components: an internal device surgically placed beneath the skin behind the ear and an external sound processor worn behind the ear. The external processor captures sound waves, converts them into digital signals, and transmits them to the implanted receiver. The receiver then stimulates the electrodes within the cochlea, the spiral-shaped inner ear cavity responsible for converting sound vibrations into electrical signals. These electrical impulses travel along the auditory nerve to the brain, where they are perceived as sound.
Implant Surgery: A Detailed Look
Surgery for Cochlear Implantation is typically performed under general anesthesia in an outpatient setting. The surgeon makes a small incision behind the ear, creating an opening in the mastoid bone to access the inner ear. The electrode array, a thin wire with multiple electrodes, is carefully inserted into the cochlea. The internal receiver is then placed in a pocket created beneath the skin. The incision is closed, and the patient is monitored for recovery.
Following a successful surgery, a period of healing and rehabilitation is crucial. After several weeks, the external sound processor is activated and programmed by an audiologist to match the specific characteristics of the individual's hearing loss. This process involves fine-tuning the device to ensure optimal sound perception and clarity.
Advantages of Surgery for Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implants offer a range of significant benefits for individuals with severe hearing loss:
- Improved hearing and speech understanding: Cochlear implants can dramatically improve the ability to hear and understand speech, both in quiet and noisy environments. This can significantly enhance communication and social interaction.
- Increased independence and quality of life: Improved hearing can lead to greater independence in daily activities, allowing individuals to participate more fully in work, social gatherings, and other aspects of life.
- Reduced social isolation: Cochlear implants can help individuals reconnect with loved ones and the world around them, reducing feelings of isolation and loneliness.
Candidates for Surgery on Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implant procedures is not suitable for everyone with hearing loss. Careful evaluation by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist and an audiologist is necessary to determine candidacy. Generally, individuals with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss who do not benefit sufficiently from hearing aids are considered potential candidates.
Factors to Consider
While surgery for cochlear implants offers significant benefits, it is important to consider several factors before undergoing the procedure:
- Risks and complications: Like any surgery, cochlear implant surgery carries potential risks, such as infection, dizziness, and facial nerve weakness.
- Cost: Cochlear implants are complex devices with associated costs for the implant itself, surgery, and ongoing maintenance.
- Realistic expectations: Cochlear implants do not restore normal hearing, but rather provide a new way to perceive sound. It takes time and dedicated rehabilitation to learn to interpret and understand sounds through the implant.
Conclusion
Surgery for cochlear implants is a remarkable advancement in medical technology that offers individuals with severe hearing loss the potential to regain a sense of sound and improve their quality of life. With careful evaluation, thorough understanding of the procedure and its outcomes, and dedicated rehabilitation, cochlear implants can significantly enhance communication, independence, and overall well-being.